Climate of the earth has never been strictly constant in the recent almost 5 billion years. The shorter or longer time changes and fluctuations lead to changes in state of the geographical skin, or, with its more recent and frequent name, the environment. This is why a fourth sub-chapter has been opened in our homepage, for the response to effects of clime given or due by the society, besides the other three ones, i.e. past, present (recent past) and future.
Climatology is embedded into various other sciences, which often leads to discussions even on the concepts of climate, as well as of climate change and fluctuation. Even more frequent and heavy discussions are observed on causes and likelihood of continuation of the present climate change, since the times we are faced to the risk of human-induced climate change. Our homepage does not intend to prefer any view or scientific result against the others in these questions. Nevertheless we still transfer a system of scientific paradigms via selection of the sites and proportions of the views reflected in this selection. But, this is definitely one of the missions of the GEOGRAPHY nEtQUIPMENT to systematise and forward that part of knowledge which has been established by the professional (not by the “official”) science.
Probably, you have already recognised, Dear Reader, that we have a separate entry called Meteorology, as well. It is not our intention, by this, to put our vote to such a classification of sciences. It has a rather practical reason, since there are so many interesting and useful sources in both topics that this may explain the separation, itself. So, materials and referring homepages about the weather, i.e. on definite sequence of the atmospheric states for shorter period of time are arranges into Meteorology. Those questions in which these states correspond to longer period of time, with no special emphasis on their sequence, but treated as statistical ensembles, i.e. to climate, we sorted into Climatology.
- Prekambric és Paleozoic (4.6 billion - 230 million years)
- Archaic Era (4.6 billion - 2,5 billion years)
- Proterozoic (2.5 billion – 545 million years)
- From Cambrian until Devonian (545 million – 360 million years)
- Carboniferous and Permian (360 million – 230 million years)
- Mesozoic and Tertiary (230 million - 2.4 million years)
- Triassic (230 million -195 million years)
- Jurasic (195 million – 145 million years)
- Cretaceous (145 million – 65 million years)
- Tertiary (65 million – 2.4 million years)
- Pleisztocene (2.4 million – 10 thousand years)
- Early Pleisztocene until Günz (2.4 million – 820 thousand years)
- Late Günz until Mindel (820 thousand – 320 thousand years)
- Late Mindel until Riss (320 thousand – 120 thousand years)
- Late Riss until Würm (120 thousand – 10 thousand years)
- Holocene (from 10 thousand years BP until Present Time)
- Climate of the Present
- Climate, climate forming factors
- Climate, its concept and spatial scales
- Spatial and temporal characteristics of the solar radiation
- Altitude and substance of the surface
- Role of atmosphere and oceans in climate formation
- Climate of the Earth
- Zonality of climate and its anomalies
- Classifications of climates in the Earth
- Climate of distant continents
- Climate of Europe
- Climate of Hungary: averages and extremities
- Solar radiation, radiation balance
- Temperature characteristics
- Precipitation and humidity conditions
- Air pressure and wind conditions
- Topo- and microclimates
- Microclimate of vegetation
- Effect of topography and exposition
- Meso- and microclimates of horizontally non-homogenous surfaces
- Indoor microclimates
- Climate of the Future
- Changes in climate forcing factors and radiation balance
- Observed changes of climate
- Modelling and understanding the climate system
- Global and regional predictions (scenarios)
- Climate impacts and response activities
- Adaptation of the Nature and the Society to the actual climate
- Effect of climate on geomorphology of the Earth
- Effect of climate on the geographical distribution of plants and animals
- Our built environment from the Equator to the Poles
- Physiological and social signals of adaptation of homo sapiens
- Impacts and adaptation challenges of the anthropogenic climate change
- Climate impacts on water resources and water demands
- Climate impacts on plants and animals
- Climate impacts on energy demands and transport
- Climate impacts on air quality and urban heat islands
- Conditions and agenda to mitigate the climate change
- Population of the earth and the per capita consumption (production)
- Energy demand of a consumption (production) unit
- Greenhouse gas emission of a unit energy consumption
- International agreements of climate change mitigation
- Impacts and responses in Hungary
- Scientific research on climate impact
- First initiatives of the intentional adaptation
- On climate mitigation
- Law sources on climate change in Hungary
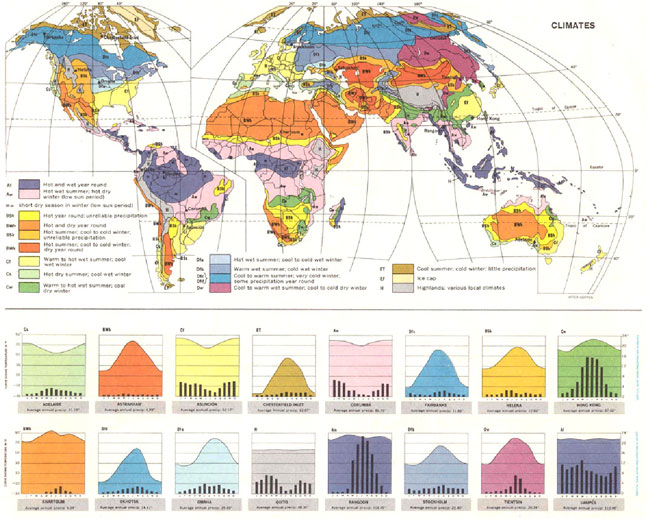
Internet source (downloaded on March 30, 2009).
http://fp.arizona.edu/kkh/climate/images/Global.climate.map.med.jpg
|





